Read our market review and find out all about our theme of the week in MyStratWeekly and its podcast with our experts Axel Botte, Aline Goupil-Raguénès and Zouhoure Bousbih.
Listen to podcast (in French only)
(Listen to) Axel Botte’s and Zouhoure Bousbih's podcast:
- Review of the week – Financial markets, economic climate in Germany, the tech bubble;
- Theme – Back to the Future for Doctor Copper!
Podcast slides (in French only)
Download the Podcast slides (in French only)Topic of the week: Back to the Future for Doctor Copper!
- The rise in copper prices reflects the structural supply deficit caused by insufficient investment in the mining industry;
- The imperative of electrification has structurally changed the global demand for the red metal;
- The rise of AI in data centers, the electric vehicle industry in the context of energy transition policies, as well as demographic and economic pressures are the three key factors determining the long-term prices of the red metal;
- Emerging copper-producing countries have a unique opportunity to strengthen their position in the global market by investing in refining infrastructure and adopting sustainable development strategies.
A Structural Deficit in Copper Supply
Copper prices on the London Metal Exchange (LME) have surged by 25% since the beginning of the year. Prices now exceed their long-term average of $7,500 per ton, as illustrated in the accompanying chart.
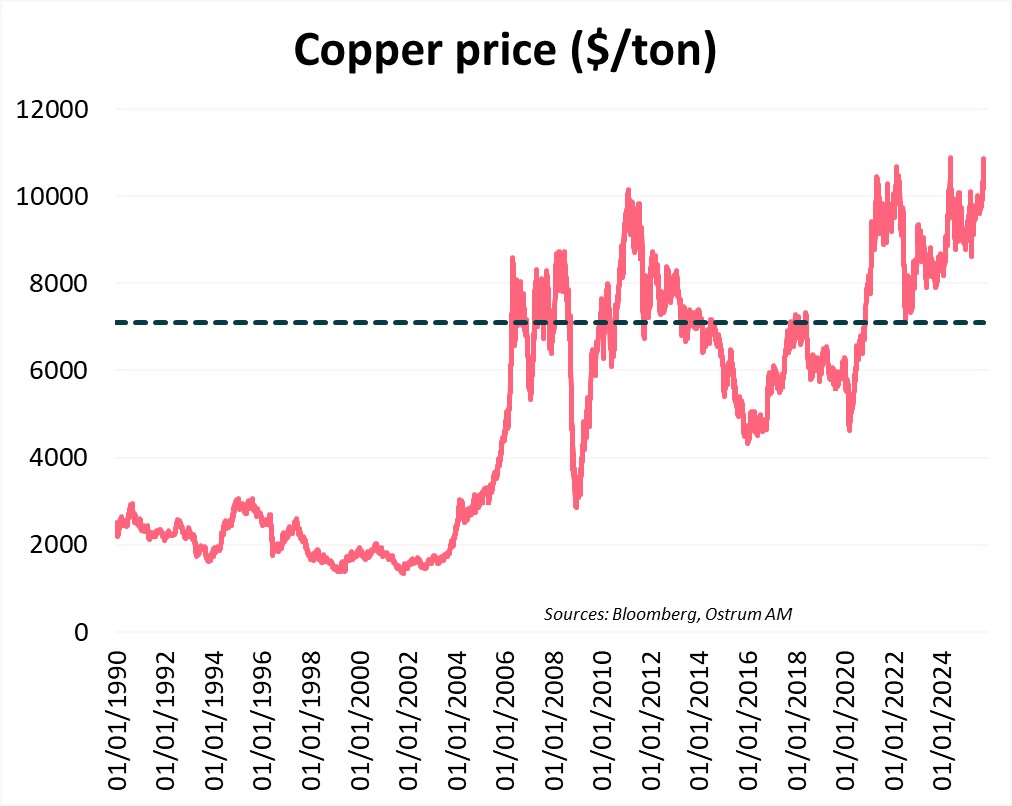
The upward trend in prices began in March 2020, driven by production chain distortions during the Covid-19 pandemic. From the low point in March 2020 to the peak in March 2022, amidst the ongoing war in Ukraine which started in February, the price of copper soared by 130%! The strong demand for copper was fueled by military needs as well as policies related to energy transition aimed at reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Among renewable technologies, the electric vehicle industry is the largest consumer of copper, accounting for 6% of global demand.
The price increase in 2025 is primarily attributed to a supply imbalance. Three of the world's major copper mines are currently shut down (Grasberg in Indonesia, Kamao-Kakula in the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Cobre Panama), representing 7% of global production. This decline in mining production coincides with an 80% drop in LME stocks this year. This supply imbalance occurs in a context where the U.S. administration has imposed a 50% tariff on copper imports, further driving up the price of the red metal.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has sounded the alarm in its latest report on global critical materials outlook, indicating that current metal supply will be 30% below the required amount by 2035 if no action is taken, as shown in the accompanying graph. The tensions in the copper market are not due to scarcity but rather to an extraction rate that does not keep up with demand.
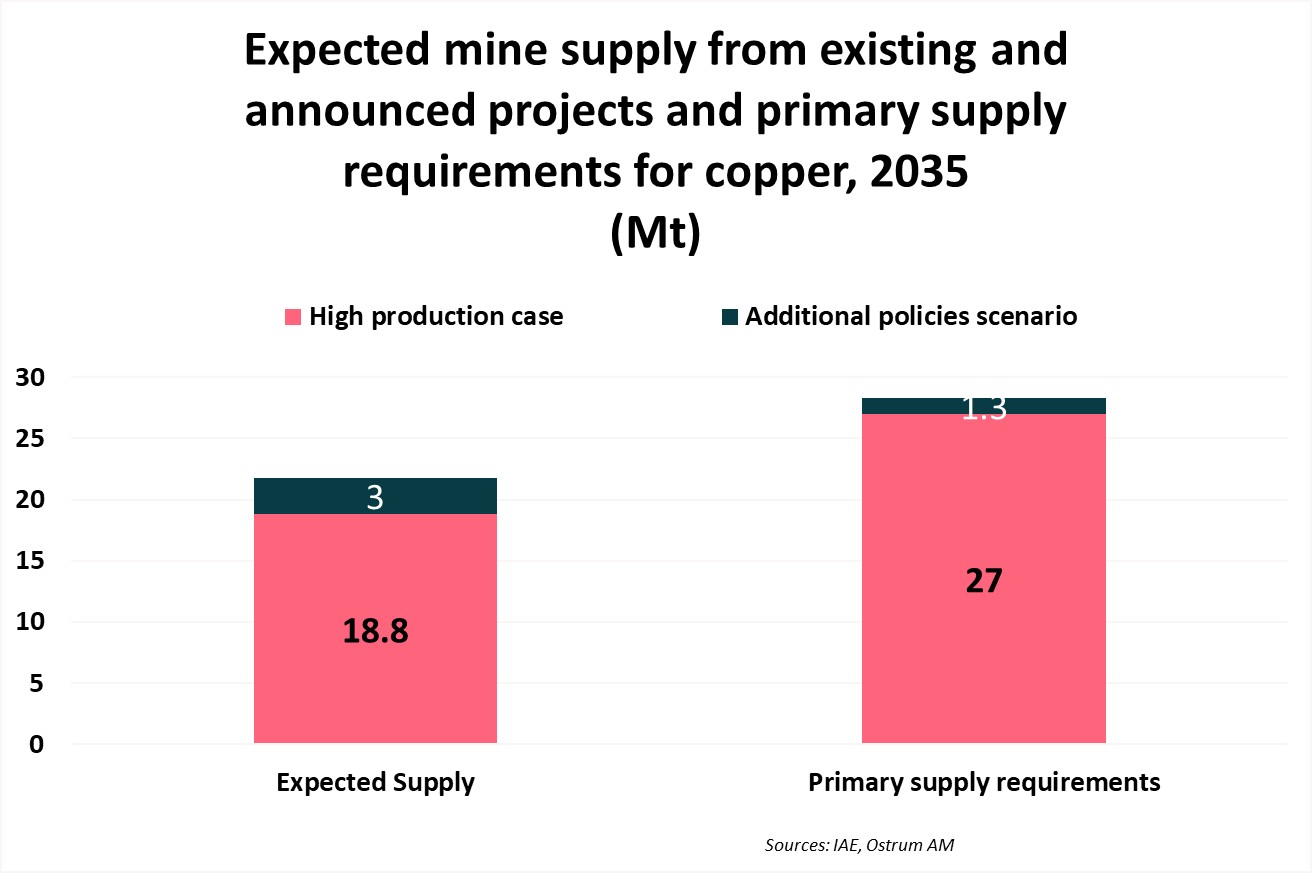
The world's largest mines are facing resource depletion, and new deposit discoveries have become rare. Over the past decade, the mining industry has focused its capital on mergers, share buybacks, and dividends, contributing little to the copper market. Furthermore, new deposit discoveries require increasingly sophisticated and costly methods as deeper deposits have lower grades compared to surface ones. The supply shortage has increased reliance on the recycled copper market. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), 44% of the copper used in the U.S. is recycled.
Electrification is a key determining factor for the outlook of the red metal.
Copper is a metal widely present in our daily lives, found in homes, smartphones, computers, and electric vehicles. It is utilized across numerous industries due to its physical properties: malleability, corrosion resistance, and particularly its thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for use in electrical wiring and electronic components. Electrification has become imperative for the global economy, driven by three key factors influencing copper price outlooks: the electric vehicle industry, AI through the expansion of data centers, and demographics.
Electric Vehicle Industry
For several years, China has been a major driver of the copper market, with its real estate sector absorbing 50% of global production. Today, China continues to play a crucial role through its electric vehicle industry, accounting for 70% of global production. Electric vehicles require three to four times more copper than internal combustion vehicles. The growth of this sector aligns with China's carbon neutrality goals by 2030. Consequently, this industry is expected to remain a significant consumer of copper (6% of global production). Since the beginning of the year, electric vehicle sales have increased by over 30% year-on-year, and this trend is expected to continue.
AI and Data Centers
A new key factor impacting copper prices is the development of data centers driven by AI. According to BloombergNEF, the electricity consumption of data centers is expected to quadruple within the next 10 years. By 2035, data centers are projected to consume 1,600 terawatt-hours, equivalent to 4.4% of global electricity production. The United States (25%) and China (25%) will account for half of the energy demand for their data centers by 2035.
Demographics
Copper prices will continue to rise, with or without AI and electric vehicles. Demographic and economic trends continue to drive demand for the red metal. China recently unveiled a new urbanization program aimed at renovating and constructing new housing in line with its low-carbon policy. Real estate projects are also multiplying across Asia, where economic growth has led to the emergence of a middle class aspiring to improve its living standards. Demographic pressures and food security policies in Africa are boosting the adoption of electronic agricultural equipment and smart irrigation systems, further intensifying copper demand.
Will Emerging Copper-Producing Countries be the Big Winners?
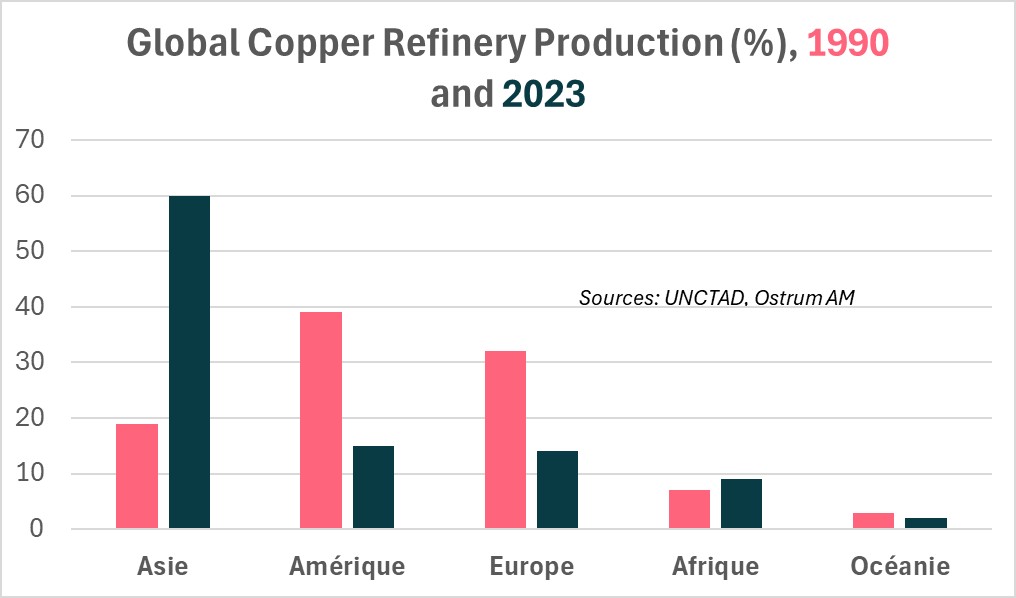
More than 50% of the world's copper reserves are concentrated in five countries: Chile (20%), Australia (10%), Peru (10%), the Democratic Republic of Congo (8%), and Russia (8%), according to data from UNCTAD. However, China imports 60% of raw copper and produces over 45% of the world's refined copper. Driven by China's influence, Asia's share in global copper refining has tripled over three decades, as shown in the accompanying chart.
Emerging countries with copper-rich soils need to invest in refining and producing higher value-added products like copper wire by strengthening their infrastructure, creating industrial parks, and implementing appropriate trade policies. For instance, Germany is the world’s leading exporter of copper wire, accounting for 13.4% of its total exports. Other countries such as the United Arab Emirates (9.4%), Canada (7%), and the United States (6.1%) also excel in this area.
Additionally, copper waste represents a strategic asset for developing countries, as it reduces dependency on imports and promotes a circular and sustainable economy.
Conclusion
Copper prices are expected to continue to rise due to the imperative of electrification. The rise of AI in data centers, the electric vehicle industry in the context of energy transition policies, as well as demographic and economic pressures are the three key factors determining the long-term outlook for the red metal's prices. Emerging copper-producing countries have a unique opportunity to strengthen their position in the global market. By investing in refining infrastructure and adopting sustainable development strategies, these countries can maximize the added value of their natural resources and contribute significantly to a circular economy. The future of copper will thus depend on the ability of stakeholders to balance extraction, technological innovation, and sustainable practices to meet global needs while preserving resources for future generations.
Zouhoure Bousbih
Chart of the week
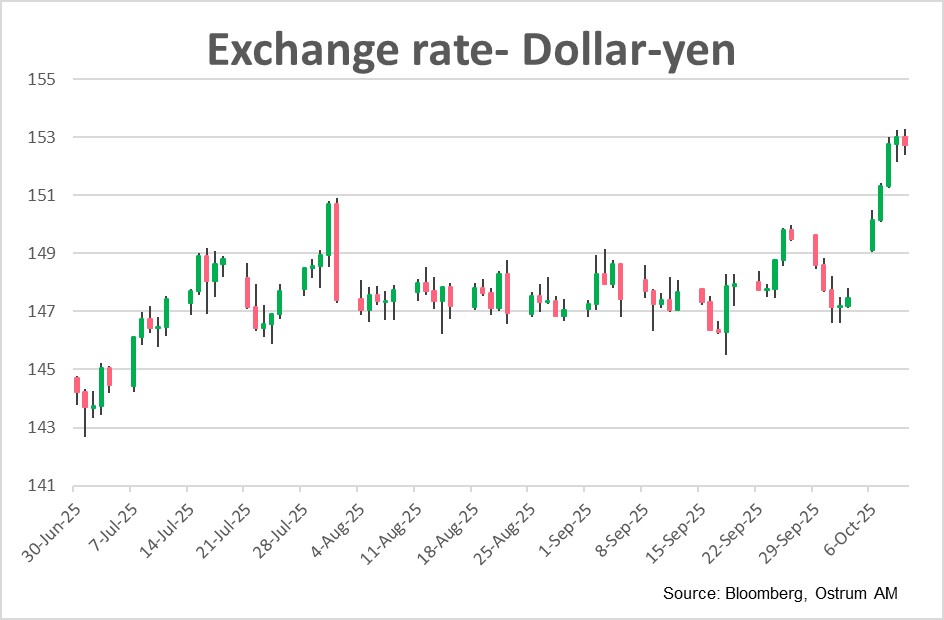
The Japanese currency has been undervalued relative to its economic fundamentals for several years. The weakness of the yen has led to increased imported inflation, which is impacting consumer confidence and was expected to result in a monetary tightening.
The hawkish bias seen at the last BoJ meeting was overshadowed by the election results of the LDP, making Sanae Takaichi the next Prime Minister of Japan. Her surprise victory triggered a sharp rise in the Nikkei and the 30-year Japanese bond yield, alongside a collapse of the yen, which fell from 147 to 153 yen per dollar within a matter of days.
The decision by Komeito to exit the ruling coalition appears to be linked to the yen's decline. Given the shutdown in the United States, the release of employment statistics will be delayed. Naturally, market attention has shifted towards surveys of businesses and households.
Figure of the week
0.5
Total uncertainty (national and otherwise) cost between 0.4 and 0.5 percentage points of GDP to French growth.
Market review:
- Trump’s renewed tariff threat sparks late selloff;
- Japan: The Nikkei rises by 5% following the victory of Sanae Takaichi, the future Prime Minister;
- France: The risk of dissolution remains pending as Mr. Lecornu is renominated;
- Currencies: The yen plunges by 4% against the greenback.
The Wall of Worries
Financial markets appear to overlook the government shutdown, U.S. cyclical risks, and the crisis in France. However, Takaichi's victory has shaken Japanese markets. The speculative bubble in tech stocks is on everyone's mind, as Trump renewed tariff threat on China sparks a sharp Nasdaq selloff.
In the absence of major data due to the shutdown, political developments have once again dominated the financial landscape. In France, Sébastien Lecornu resigned, early on last week, only to be renominated by President Macron days later with the hope to avoid a dissolution of the National Assembly. In Japan, Sanae Takaichi's election victory within the LDP significantly impacted markets, triggering a strong rebound in the Nikkei, coupled with a surge in long-term rates (the 30-year JGB surpassing 3.30% at its peak) and a notable drop in the yen. Gold has breached the $4,000 mark per ounce, lifting all precious and industrial metals in its wake. The dollar has strengthened despite an unfavorable environment for fiat currencies. Speculative bullishness in equity markets remains robust, particularly for U.S. technology stocks. The bubble is widely recognized, and the market reaction to Trump’s latest salvo against China shows the fragility of equity valuations (Nasdaq closed down 3.5 % on Friday).
From a cyclical perspective, the limited U.S. data available paints a mixed picture. Consumer credit stalled in August, contradicting the rebound in private consumption observed in July and August. The labor market is also contracting. However, consumption from the top decile by income represents half of total household spending, and rising stock prices may have also spurred consumer expenditure. In the Eurozone, industrial orders in Germany and the subsequent production have sharply declined mid-summer. The rollout of public investments has yet to impact the German economic landscape. In France, surveys reflect the dampening effect of political uncertainty, which could cost as much as 0.4 percentage points of growth, according to the Bank of France.
Financial markets were still favorable for risk assets until Donald Trump’s intervention. The Nikkei up 5% thanks to the dollar-yen adjustment (reaching 153.27 at the week's peak), propelled the South Korean Kospi, which has gained 50% since the beginning of the year. Western markets were stable until Donald Trump tariff announcement, as major indices lost 2 to 3% last week. In the euro area, the DAX is outperforming despite weak data out of Germany. Defensive sector stocks (utilities, consumer staples) continue to be favored in the Eurozone. In the bond markets, the Bund fluctuates around 2.70% before rallying to a 2.64 % close while the T-note broke below 4.10% to close at 4.03%. The decline in bank reserves below the $3 trillion mark is creating sporadic pressures on SOFR, which tend to widen USD swap spreads. Conversely, euro swap spreads rose back in positive territory on 10-year maturities. The political crisis in France has had minimal impact on the OAT, which trades just above 80 bps. Whilst the attempt to avoid snap elections may mean that fiscal consolidation will be delayed. Overall, sovereign spreads have remained stable. In the credit market, spreads remain tight about 70 bps over swaps. Despite the summer tightening, credit still presents relative appeal. However, the trend toward widening is gaining momentum in the high yield segment, which has widened by 34 bps over the past week. Profit-taking is likely to accumulate as the year draws to a close.
Axel Botte
Main market indicators